The current ratio (also known as the current asset ratio, the current liquidity ratio, or the working capital ratio) is a financial analysis tool used to determine the short-term liquidity of a business. It takes all of your company’s current assets, compares them to your short-term liabilities, and tells you whether you have enough of the former to pay for the latter. The current ratio formula is essential to evaluate whether a company’s liquid assets are sufficient to settle its obligations. To maintain a good ratio, the company must ensure that it utilizes its assets efficiently and maintains a balance where current assets equal or exceed current liabilities. Therefore, paying attention to the current ratio is crucial if a company wants to avoid accumulating debts and obligations.
It is simply calculated by dividing a company’s total assets (cash and easily convertible assets) by its short-term debts (accounts payable for the year). Once you’ve calculated the current ratio, you can draw inferences about the company. Also consider how the current ratio has changed over time and what that might mean for a company’s trajectory. For very small businesses, calculating total current assets and total current liabilities may not be an overwhelming endeavor. As businesses grow, however, the number and types of debts and income streams can become greatly diversified. Microsoft Excel provides numerous free accounting templates that help to keep track of cash flow and other profitability metrics, including the liquidity analysis and ratios template.
Benefits and limitations of using current ratio
With that said, the required inputs can be calculated using the following formulas. Average values for the ratio you can find in our industry benchmarking reference book – Current ratio. We do not manage client funds or hold custody of assets, we help users connect with relevant financial advisors. An author, teacher & investing expert with nearly two decades experience as an investment portfolio manager and chief financial officer for a real estate holding company.
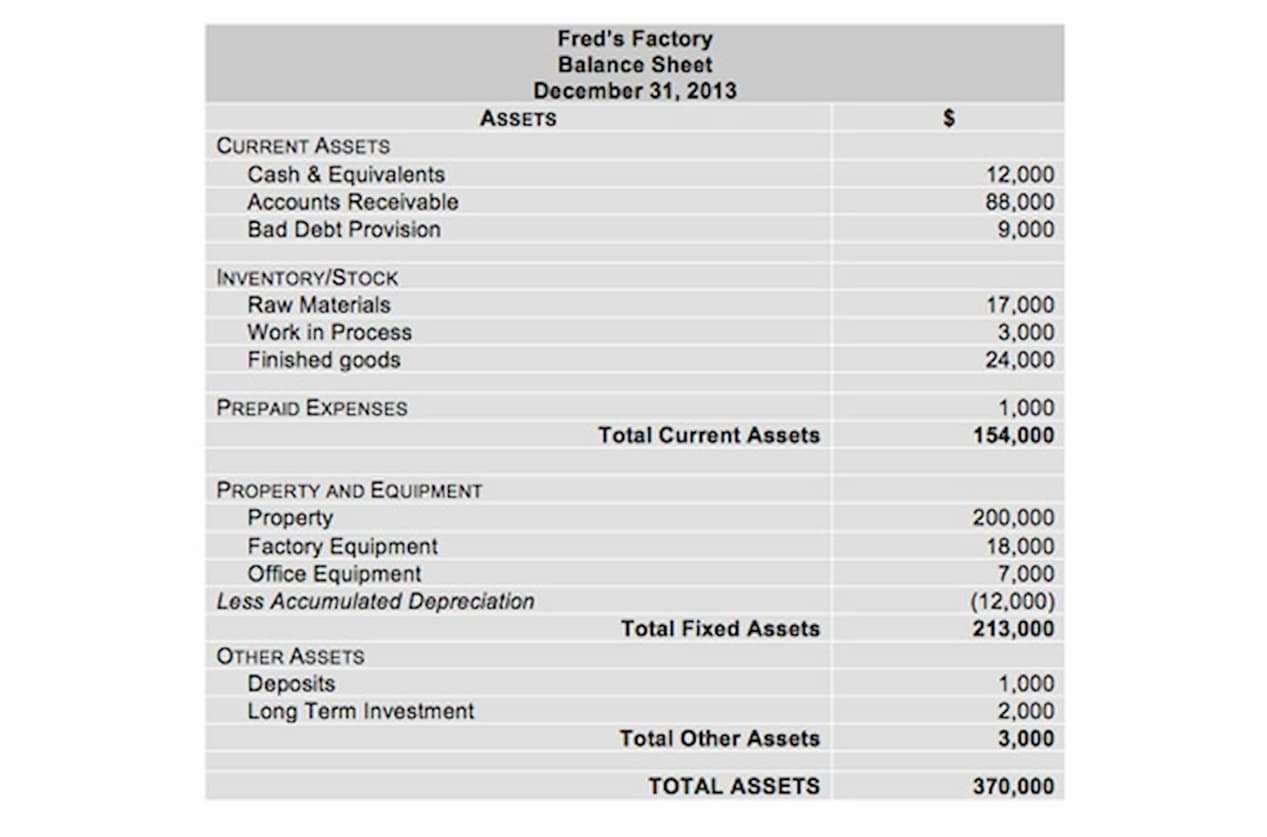
- Current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used to pay off short-term obligations within one year.
- When evaluating a company’s working capital ratio, it is important to look at how the ratio changes over time.
- It indicates the financial health of a company and how it can maximize the liquidity of its current assets to settle debt and payables.
- For example, consider prepaid assets that a company has already paid for.
- To use the current ratio to make business decisions, you need to understand the balance sheet and the accounts that make up the balance sheet.
- In these situation, it may not be possible to calculate the quick ratio.
Their findings indicate that current ratio and quick ratio have a positive correlation with profitability, while cash ratio has a negative correlation. This suggests that a higher current ratio and quick ratio increase profitability, while a higher cash ratio decreases profitability. Furthermore, the study found that the correlation between profitability and liquidity ratios is stronger for firms with higher leverage. This indicates that liquidity ratios are especially important for highly leveraged firms.
Small business balance sheet template
In this article, we will delve into what the current ratio is, why it is significant, and how it’s calculated. Other measures of liquidity and solvency that are similar to the current ratio might be more useful, depending how to calculate current ratio on the situation. For instance, while the current ratio takes into account all of a company’s current assets and liabilities, it doesn’t account for customer and supplier credit terms, or operating cash flows.
- The company has just enough current assets to pay off its liabilities on its balance sheet.
- “Expert verified” means that our Financial Review Board thoroughly evaluated the article for accuracy and clarity.
- However, the company’s liability composition significantly changed from 2021 to 2022.
- The current ratio measures a company’s capacity to meet its current obligations, typically due in one year.
- Liquidity is the ability to generate enough current assets to pay current liabilities, and owners use working capital to manage liquidity.
- But, by examining its balance sheet, we understand that the ratio is high because of Company Y’s high inventory.
The quick ratio measures a company’s liquidity based only on assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days or less. Since the current ratio compares a company’s current assets to its current liabilities, the required inputs can be found on the balance sheet. The formula to calculate the current ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. Other similar liquidity ratios can supplement a current ratio analysis.
The five major types of current assets are:
The company has just enough current assets to pay off its liabilities on its balance sheet. If a company’s current ratio is less than one, it may have more bills to pay than easily accessible resources to pay those bills. What counts as a good current ratio will depend on the company’s industry and historical performance.

Both ratios include accounts receivable, but some receivables might not be able to be liquidated very quickly. As a result, even the quick ratio may not give an accurate representation of liquidity if the receivables are not easily collected and converted to cash. A company’s current ratio will often be higher than its quick ratio, as companies often use capital to invest in inventory or prepaid assets. While the current ratio is an effective measure of the short-term liquidity of a company, it is important to use other liquidity measures when evaluating a company. The current ratio is unable to provide a prospective investor with other important metrics such as solvency, profitability, and growth metrics.
Large companies often have higher current ratios due to their high revenue generation. The current ratio is used to evaluate a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations, such as accounts payable and wages. The higher the result, the stronger the financial position of the company. The current ratio is one of multiple financial ratios used to assess the financial health of a company. Specifically, the current ratio expresses a business’ ability to pay back short-term debt using only current assets.
Empower yourself with the knowledge to navigate the complex terrain of financial analysis confidently. The current ratio does not inform companies of items that may be difficult to liquidate. For example, consider prepaid assets that a company has already paid for. It may not be feasible to consider this when factoring in true liquidity as this amount of capital may not be refundable and already committed.